JavaScript_course
Traversing the DOM
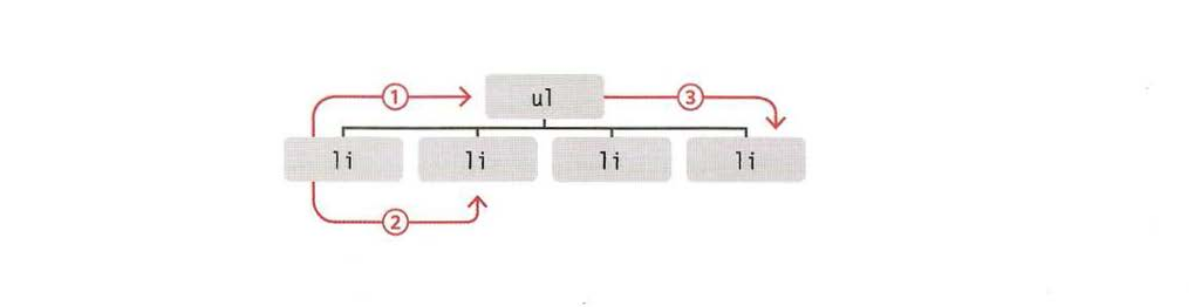
When you have an element node, you can select another element in relation to it using these five properties (grouped in 3 categories in relation). This is known as traversing t he DOM.
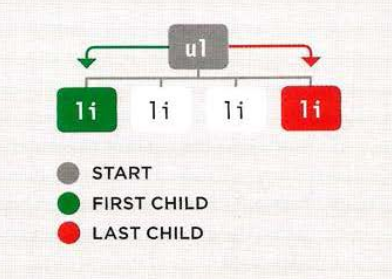
parentNodeto get the container element.previousSibling,nextSiblingto get previous or next element of according to the current element.firstChild,lastChildto get the first or last element inside the container of elements.
WHITESPACE NODES
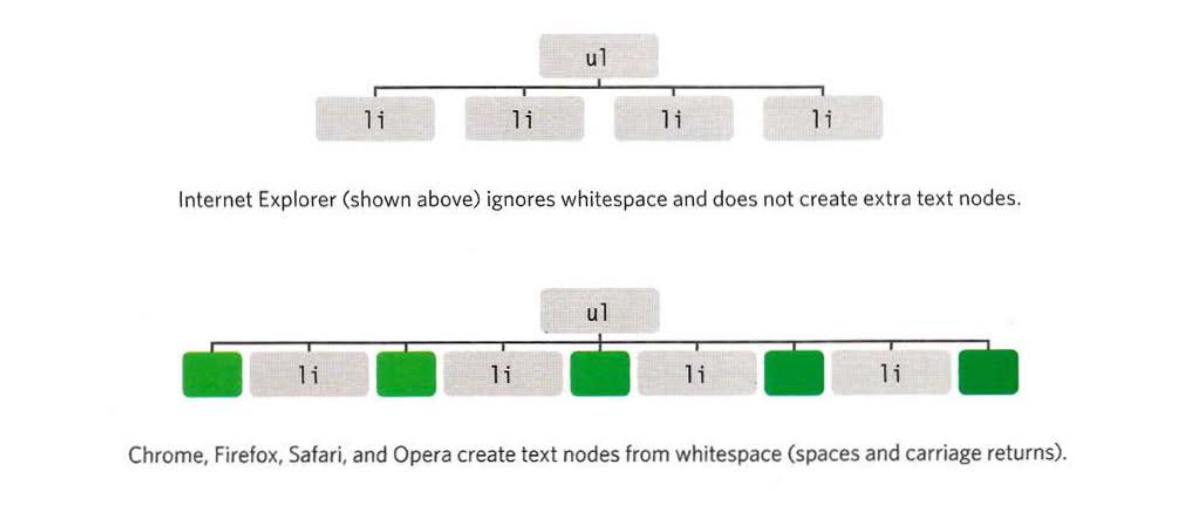
Traversing the DOM can be difficult because some browsers add a text node whenever they come across whitespace between elements.
Let us see the same example about HTML and CSS
HTML
<ul>
<li id="one" class="hot"><em>fresh</em> figs</li>
<li id="two" class="hot">pine nuts</li>
<li id="three" class="hot">honey</li>
<li id="four">balsamic vinegar</li>
</ul>
CSS
@import url(http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Oswald);
body {
background-color: #000;
font-family: "Oswald", "Futura", sans-serif;
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
#page {
background-color: #403c3b;
margin: 0px auto 0px auto;
}
/* Responsive page rules at bottom of style sheet */
h1 {
background-image: url(../images/kinglogo.png);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center center;
text-align: center;
text-indent: -1000%;
height: 75px;
line-height: 75px;
width: 117px;
margin: 0px auto 0px auto;
padding: 30px 10px 20px 10px;
}
h2 {
color: #fff;
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: normal;
text-align: center;
text-transform: uppercase;
letter-spacing: 0.2em;
margin: 0px 0px 23px 0px;
}
h2 span {
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: #000;
font-size: 10px;
text-align: center;
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
top: -5px;
height: 18px;
width: 20px;
margin-left: 5px;
padding: 4px 0px 0px 4px;
}
ul {
background-color: #584f4d;
border: none;
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
}
li {
background-color: #ec8b68;
color: #fff;
border-top: 1px solid #fe9772;
border-bottom: 1px solid #9f593f;
font-size: 24px;
letter-spacing: 0.05em;
list-style-type: none;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #9f593f;
height: 50px;
padding-left: 1em;
padding-top: 10px;
}
.hot {
background-color: #d7666b;
color: #fff;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #914141;
border-top: 1px solid #e99295;
border-bottom: 1px solid #914141;
}
.cool {
background-color: #6cc0ac;
color: #fff;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #3b6a5e;
border-top: 1px solid #7ee0c9;
border-bottom: 1px solid #3b6a5e;
}
.complete {
background-color: #999;
color: #fff;
background-image: url("../images/icon-trash.png");
background-position: center right;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #ccc;
border-top: 1px solid #666;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #333;
}
li a {
color: #fff;
text-decoration: none;
background-image: url("../images/icon-link.png");
background-position: center right;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
padding-right: 36px;
}
p {
color: #403c3b;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 5px;
text-align: center;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px auto 20px auto;
min-width: 20%;
max-width: 80%;
}
#scriptResults {
padding-bottom: 10px;
}
/* Small screen - acts like the app would */
@media only screen and (max-width: 500px) {
body {
background-color: #584f4d;
}
#page {
max-width: 480px;
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 501px) and (max-width: 767px) {
#page {
max-width: 480px;
margin: 20px auto 20px auto;
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 959px) {
#page {
max-width: 480px;
margin: 20px auto 20px auto;
}
}
/* Larger screens act like a demo for the app */
@media only screen and (min-width: 960px) {
#page {
max-width: 480px;
margin: 20px auto 20px auto;
}
}
@media (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2), (min-resolution: 192dpi) {
h1 {
background-image: url(../images/2xkinglogo.png);
background-size: 72px 72px;
}
}
Let us see example found in example found in Chapter_05/Examples/c05/node-list.html
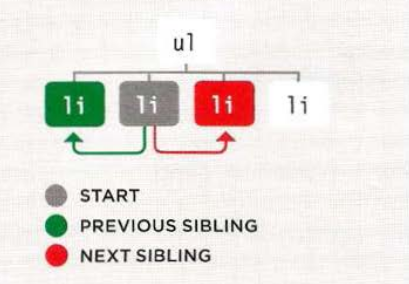
Apply previous & next sibling script
JavaScript
// Select the starting point and find its siblings.
var startItem = document.getElementById("two");
var prevItem = startItem.previousSibling;
var nextItem = startItem.nextSibling;
// Change the values of the siblings' class attributes.
prevItem.className = "complete";
nextItem.className = "cool";
Apply first & last child script
JavaScript
// Select the starting point and find its siblings.
var startItem = document.getElementById("two");
var prevItem = startItem.previousSibling;
var nextItem = startItem.nextSibling;
// Change the values of the siblings' class attributes.
prevItem.className = "complete";
nextItem.className = "cool";